The New Electric Cars are Taking Over: Buckle Up for a Sustainable Ride!
The New Electric Cars has become an important alternative as traditional combustion engine vehicles face limited fossil fuel resources and environmental concerns. This article will highlight the technological advancements powering the electric car revolution, ranging from advances in battery technology to the creation of effective charging infrastructure.
Nowadays, the auto industry is experiencing an evolution that includes a significant shift toward electric cars (ECs). The goal of this blog post is to examine the state-of-the-art of this development, with a particular emphasis on the latest developments in electric vehicles, popular market trends, and the future of sustainable mobility.

Additionally, we will look at the dynamic market environment and analyze how government programs, industry alliances, and consumer preferences are influencing electric car trends. The blog post will shed light on how these variables are affecting the general course of the automotive sector and the strategies used by key companies to adjust to this paradigm shift.
In conclusion, the conversation will cover the future of sustainable mobility, with a focus on how electric cars can impact energy efficiency, low carbon emissions and the automotive industry. It seeks to give readers a holistic picture of the electric vehicle market as well as provide practical information on the ongoing revolution shaping the direction of transportation.
The Rise of Electric Cars: A Paradigm Shift
1.1 The Environmental Imperative
The imperative to reduce emissions and tackle climate change has become even greater in the face of growing environmental challenges. The discussion will address the critical need for urgent action to curb emissions, highlighting the far-reaching consequences of climate change and the global mandate to mitigate its impacts. From rising sea levels and extreme weather events to biodiversity loss, the harmful effects of climate change are evident around the world. The discourse will emphasize the importance of adopting sustainable practices, transitioning to clean energy sources and implementing effective policies to achieve emission reduction targets. Ultimately, the urgency arises from the realization that collective efforts are essential to safeguard the future of the planet, and that failure to act immediately could result in irreversible damage to ecosystems and jeopardize the well-being of current and future generations.
1.2 The EC Revolution
- The adoption of new electric cars (ECs) is increasing significantly globally, signaling a paradigm shift in the automotive industry. This exploration will explore the rapid growth in EC adoption globally, examining the key drivers fueling this growth. From advances in battery technology and decreasing costs to environmental awareness and government initiatives, various factors contribute to the growing popularity of new electric car. The discussion will also discuss the diverse regional trends and market dynamics that shape the EC adoption landscape. As more countries commit to sustainable transportation and automakers invest heavily in electric mobility, understanding the accelerating pace of EC adoption provides valuable insight into the automotive sector’s transformative future.
In the Electric Cars (ECs) scenario, key statistical indicators related to sales, charging infrastructure and government incentives play an important role. This introduction will highlight the current status of these aspects, providing a snapshot of the global landscape.
First, examining EC sales data reveals a rising trend as more consumers adopt sustainable transportation options. The significant increase in electric vehicle purchases underlines the growing preference towards clean and green mobility solutions.
Secondly, expanding charging infrastructure is a critical component for widespread adoption of ECs. Data from the region will demonstrate the proliferation of charging stations, reflecting efforts to address range anxiety and make electric vehicles more practical for daily use.
Finally, government incentives have a substantial impact in shaping the EC landscape. Data on tax credits, subsidies and policy support will be explored to show how different countries are encouraging the shift to electric vehicles, driving market growth.
Looking at these data provides a comprehensive understanding of the current state and trajectory of electric cars, providing valuable insight into the dynamics of this rapidly growing sector.
2. The Anatomy of a Modern Electric Cars
2.1 Battery Technology
The detailed exploration of lithium-ion batteries reveals their vital role revolutionizing the automotive industry, especially in the field of new electric cars (ECs). This discussion will shed light on the complexities of lithium-ion batteries, analyzing their impact on important aspects such as range, charging speed and overall performance. Revolutionizing the automotive industry, especially in the field of electric cars (ECs). This discussion will shed light on the complexities of lithium-ion batteries, analyzing their impact on important aspects such as range, charging speed and overall performance.

Lithium-ion batteries have become the standard power source for Electric Cars due to their high energy density and efficiency. Examining their impact on the range of electric cars highlights the important relationship between battery capacity and the distance a car can travel on a single charge. Technological advancements in lithium-ion batteries have substantially increased the range of ECs, addressing one of the primary concerns hindering their widespread adoption.
Additionally, the discussion will also discuss the importance of lithium-ion batteries in determining charging speed. Innovations in battery technology directly impact the time it takes to charge an new electric cars, impacting the convenience and practicality of EC ownership.
Ultimately, an analysis of overall performance, including factors such as durability, weight, and cost, will provide a comprehensive understanding of how lithium-ion batteries serve as the cornerstone for the success and advancement of new electric cars.
By examining these aspects in depth, we gain insight into the transformative impact of lithium-ion batteries, highlighting their critical role in shaping the future of electric mobility.
Solid-state batteries and their potential game-changing effects.
The electric cars (EC) landscape is witnessing a significant technological leap with innovations such as solid-state batteries offering the potential for game-changing impacts in the automotive industry. This discussion will explore the emergence of solid-state batteries and their transformative impact on various aspects of electric mobility.
Solid-state batteries represent a radical departure from traditional lithium-ion counterparts by replacing liquid electrolytes with solid materials. This innovation addresses critical challenges such as energy density, safety and charging time. The introduction of solid-state batteries promises to significantly increase the range of electric vehicles, effectively mitigating one of the primary limitations hindering widespread adoption.
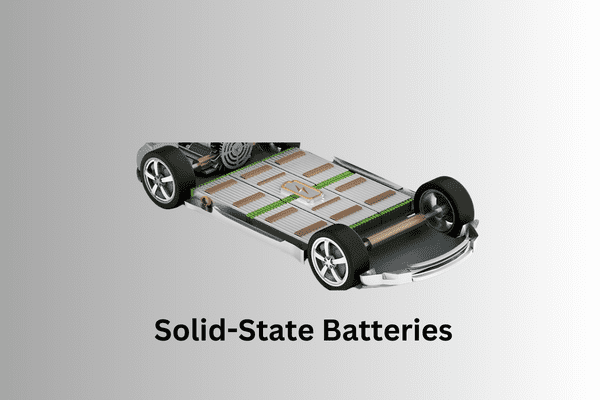
Additionally, the potential game-changing impacts extend to safety improvements, as solid-state batteries are inherently less prone to overheating and combustion risks than liquid electrolyte batteries. This aspect not only enhances the safety of electric vehicles but also contributes to building consumer confidence in the technology.The discussion will also discuss economic and environmental impacts, considering the potential for reduced manufacturing costs, increased energy efficiency, and reduced dependence on scarce resources.In short, the discovery of innovations like solid-state batteries offers a glimpse of a future where electric cars can redefine the automotive landscape, transcend existing limitations, and usher in a new era of sustainable, efficient, and safe transportation.
2.2 Electric Motors and Efficiency
Electric motors work on the principle of electromagnetic induction to produce motion. Here’s a simple explanation of how electric motors work and what advantages they have over internal combustion engines:
Basic operation:
An electric motor consists of a rotor (or armature), a stator, and a power supply. The rotor contains coils or windings, while the stator produces a magnetic field.
When electric current flows through the coils in the rotor, it creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the magnetic field generated by the stator, producing a force that causes the rotor to rotate.
Advantages over internal combustion engines:
Efficiency: Electric motors are highly efficient in converting electrical energy into mechanical energy. They can achieve much higher efficiency levels than internal combustion engines.
Instant Torque: Electric motors deliver maximum torque instantly, providing instant acceleration and responsive performance. This characteristic makes electric cars (ECs) particularly agile in urban environments.
Simplicity and fewer moving parts: Electric motors have fewer moving parts than internal combustion engines. This simplicity results in reduced maintenance requirements and increased reliability.
Reduced environmental impact: Electric motors produce no tailpipe emissions, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable transportation ecosystem. When combined with renewable energy sources, electric vehicles can significantly reduce the overall carbon footprint.
Regenerative braking: Electric motors can act as generators during braking, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy. This regenerative braking system improves overall energy efficiency and extends the range of the vehicle.
While internal combustion engines have been dominant for many years, the advantages of electric motors are driving the shift toward electric car as the automotive industry adopts more sustainable and efficient transportation solutions.
Electric Motors:
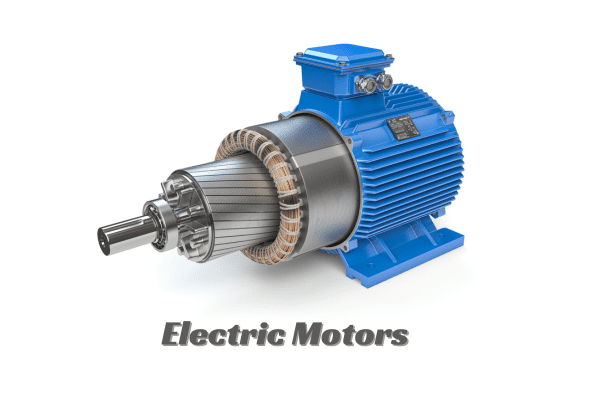
Electric motors are highly efficient at converting electrical energy into mechanical energy. They can typically achieve efficiency levels above 90%, with some electric vehicles (EVs) reaching over 95% efficiency.The efficiency of electric motors remains relatively consistent across a wide range of operating speeds, contributing to their effectiveness in a variety of driving conditions.
Internal combustion engines: Internal combustion engines (ICE) have lower efficiency than electric motors. Traditional gasoline engines typically operate at efficiency levels around 20–30%, with some advanced combustion technologies reaching higher, but still generally lower than electric motors.ICE efficiency can be affected by factors such as engine speed, load and driving conditions, causing variations in fuel efficiency.
Torque: Electric Motors:The electric motors deliver maximum torque instantly from zero rpm, providing quick and responsive acceleration. This feature is beneficial for city driving and overall driving performance.
The torque curve of electric motors is generally flat, ensuring consistent and strong torque delivery across a wide range of speeds.
internal combustion engines:
Internal combustion engines often exhibit a torque curve with a peak at a specific rpm range. Torque delivery in a conventional gasoline engine is less immediate than that of an electric motor.
While advanced technologies such as turbocharging can improve low-end torque, the overall torque characteristics of an internal combustion engine can vary depending on engine design and tuning.
Maintenance Requirements:
Electric Motors:
Electric motors have fewer moving parts than internal combustion engines. As a result, they generally require less maintenance.
Maintenance tasks for electric vehicles (EVs) often involve components such as batteries, which can degrade over time and require replacement. However, routine tasks such as oil changes, which are common in internal combustion engines, are not necessary for electric motors.
Internal combustion engines:
Internal combustion engines have more complex systems with various moving parts, such as pistons, crankshafts, and valves. This complexity can lead to higher frequency of maintenance requirements.
Routine maintenance of internal combustion engines includes oil changes, air filter replacement and tune-ups to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
In short, electric motors generally outperform internal combustion engines in terms of efficiency and torque delivery, while also requiring less maintenance due to their simple mechanical structure. These factors contribute to the growing popularity of electric vehicles, especially in terms of sustainability and overall driving experience.
Aerodynamics: Importance: Aerodynamics is an important aspect of vehicle design that focuses on reducing air resistance or drag. Efficient aerodynamics contribute to fuel efficiency and overall performance by reducing the energy required to move through the air.
Design elements: Streamlined shapes, sloping rooflines and smooth surfaces are common design elements aimed at improving aerodynamics. These features help the vehicles penetrate the air with minimum resistance.
Technological advancements: Advanced simulation and wind tunnel testing are employed to optimize the vehicle’s shape for aerodynamic efficiency. Features such as active aerodynamics, such as adjustable spoilers, are being integrated to dynamically adapt to driving conditions.
Light material: Importance: The use of lightweight materials is important to improve fuel efficiency, enhance performance and extend the range of electric vehicles. Lighter vehicles require less energy to accelerate and decelerate.
Ingredients used: Aluminium, carbon fiber, high-strength steel, and composite materials are commonly used to reduce the weight of vehicle components. These materials maintain structural integrity while providing significant weight savings.
Innovation: Ongoing research and development is focused on creating advanced lightweight materials with improved strength and durability. This involves the exploration of new alloys, composite structures and manufacturing techniques to achieve a balance between weight reduction and safety.
Futuristic Design:New Concepts:Futuristic vehicle designs often push the boundaries of traditional aesthetics, exploring unique shapes, unconventional cabin layouts, and even autonomous features. Concepts like flying cars and modular vehicles demonstrate futuristic thinking.
Integration of Technology:Futuristic designs often integrate cutting-edge technologies, including augmented reality displays, AI-powered user interfaces, and advanced connectivity. The goal is to create a seamless and immersive driving experience.
Stability Focus:Many futuristic designs prioritize sustainability by incorporating eco-friendly materials, renewable energy sources, and emphasizing recycling. This is in line with the increasing emphasis on environmentally conscious transportation solutions.
In short, the exploration of aerodynamics, lightweight materials, and futuristic designs represent the continuing evolution of automotive engineering. The integration of these elements not only improves performance and efficiency but also shapes the visual and experiential aspects of vehicles, setting the stage for the future of transportation.
2.3 Cutting-Edge Design and Materials
Showcase EC models that push the boundaries of aesthetics and functionality.
Tesla Model S:
- The Tesla Model S is famous for its sleek and minimalist design. With a focus on aerodynamics, it combines high performance with a stylish exterior. Its large touchscreen interface, autopilot capabilities and constant over-the-air updates demonstrate advanced functionality.

Porsche Taycan:
- Porsche’s Taycan represents a blend of electric power and sports car performance. It features a distinctive design that retains the iconic aesthetics of Porsche while introducing innovative technology. The Taycan emphasizes both speed and luxury, setting new standards for electric sports cars.

Audi e-tron GT:
- The Audi e-tron GT is characterized by its dynamic and elegant design. As a high-performance electric grand tourer, it demonstrates Audi’s commitment to matching electric mobility with sophisticated aesthetics. The interior incorporates state-of-the-art technology and high-quality materials.

Rivian R1T and R1S:
- Rivian’s R1T electric pickup truck and R1S electric SUV challenge traditional notions of electric vehicles. With robust and bold designs, these models meet the needs of outdoor enthusiasts. Apart from their aesthetic appeal, they also offer impressive off-road capabilities and practical functionality.

Lucid Air:
- The Lucid Air is a luxury electric sedan that exemplifies modern elegance. Its spacious interior, high-resolution display and attention to detail redefine the luxury electric vehicle segment. The Air’s aerodynamic design contributes to both efficiency and aesthetics.

NIO ES8:
- The NIO ES8 is an electric SUV from Chinese automaker NIO, which combines an attractive exterior with advanced technology. Its distinctive front-end design and spacious, tech-based interior contribute to its appeal. NIO’s battery-swapping technology adds a layer of innovation to its functionality.

Cybertruck by Tesla:
- Tesla’s Cybertruck is a marked departure from traditional truck design. With its angular, stainless steel exoskeleton, it challenges preconceived notions of what a pickup truck should look like. Its unconventional design paired with strong functionality and off-road capabilities.
- These electric vehicle models not only demonstrate advancements in sustainable transportation but also redefine the boundaries of aesthetics and functionality in the automotive industry. As innovation continues, the convergence of cutting-edge technology and distinctive design elements is shaping the future of electric mobility.

Charging Infrastructure: The Backbone of EVs
3.1 Home Charging Solutions
Home Charging Stations (Level 1 and Level 2).
- Installing a home charging station for electric vehicles is a convenient and practical way to make sure your vehicle is ready to go when you need it. There are two main levels of home charging: Level 1 (120V) and Level 2 (240V). Here’s a guide to help readers set up both types of home charging stations:
- Level 1 Home Charging (120V):
- Requirements:
- Standard Electrical Outlet:
- Use a grounded, three-pronged 120V electrical outlet. Make sure it is in good condition and meets local electrical codes.
- Portable Charging Cable (EVSE):
- Most electric vehicles come with a portable Level 1 charging cable, also known as an electric vehicle service device (EVSE). Plug one end into your vehicle and the other end into a standard outlet.
- Dedicated Circuit (optional):
- Although it is not always necessary, consider using a dedicated circuit for charging your EV to avoid overloading the existing circuit. If necessary, consult an electrician for this.
- Installation Steps:
- Find an outlet:
- Identify a convenient and accessible standard electrical outlet near your parking space.
- Plug-in EVSE:
- Plug the Level 1 EVSE into your electric vehicle’s outlet and charging port.
- Charging:
- Start charging your electric vehicle. Level 1 charging is slower than Level 2, but is suitable for overnight charging or for people with limited charging needs.
Level 2 Home Charging (240V):
Requirements:240V outlet or charging station:
- Install a 240V outlet or a dedicated Level 2 charging station. Consult a licensed electrician to ensure proper installation and compliance with local codes.
- EVSE Unit:
- Purchase a Level 2 EVSE unit compatible with your electric vehicle. These units provide faster charging than Level 1.
- Professional installation (recommended):
- For Level 2 charging stations, professional installation by a licensed electrician is recommended. This ensures safety and compliance with local regulations.
- Installation Steps:
- choose location:
- Choose a location close to your parking space, but also accessible to a 240V outlet or installation of a charging station.
- Install a 240V outlet or charging station:
- If installing a 240V outlet, an electrician will install the outlet and ensure it has the required amperage for your EVSE. For the charging station, it will be securely mounted on a wall or post.
- Connect EVSE:
- Connect the Level 2 EVSE to a 240V outlet or charging station. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper setup.
- Charging:
- Plug the Level 2 EVSE into your electric vehicle and start charging. Level 2 charging significantly reduces charging time compared to Level 1.
- By following these steps and consulting professionals when needed, readers can set up a convenient and efficient home charging station for their electric vehicles. Regularly check for updates from your vehicle manufacturer and EVSE provider for optimal charging practices.
- Discuss the convenience and cost-effectiveness of charging at home.
- Charging electric vehicles (EVs) at home offers significant convenience and cost-effectiveness, contributing to the appeal of owning an electric car. Here are the main points to consider:
- Convenience:
- Accessibility: Home charging provides the convenience of charging your EV at any time, eliminating the need to visit public charging stations. This is especially beneficial for the daily commute, as your vehicle starts every day with a full or nearly full battery.
- Flexibility: Home charging allows you to integrate charging into your daily routine. You can plug your EV in overnight, taking advantage of off-peak electricity rates, and have a fully charged vehicle ready for the day.
- No queues or waiting time: Unlike public charging stations, there is no need to wait in line to charge your vehicle at home. This eliminates potential inconveniences associated with crowded charging locations.
- Cost-Effectiveness:
- Lower cost per charge: Home electricity rates are generally lower than the cost per kilowatt-hour at public charging stations. This makes charging at home more cost effective in the long run.
- No subscription fees: Many public charging networks require a membership or subscription fee. Home charging eliminates these additional costs, making it a simpler and potentially more affordable solution.
- Installation costs: Although there may be an initial investment in a home charging station, over time, the cost can be offset by savings compared to public charging fees.
- Charging Infrastructure:
- Investment in infrastructure: Public charging infrastructure is constantly improving, but availability may vary depending on location. In contrast, the infrastructure for home charging is relatively simple, requiring a dedicated electrical circuit and a home charging station.
- Customization: Homeowners have the flexibility to choose the type of charging station to suit their needs and budget, ranging from basic Level 1 chargers to faster Level 2 chargers.
- Environmental Impact:
- Renewable energy potential: Homeowners can choose to power their home charging stations from renewable energy sources, thereby reducing the overall environmental impact of EV use.
- In short, charging at home offers unparalleled convenience and cost-effectiveness for EV owners. While there may be an initial investment in home charging infrastructure, the long-term savings, along with the flexibility and accessibility, make it an attractive option for many electric vehicle users.
3.2 Public Charging Networks
- Highlight the importance of expanding public charging infrastructure.
- Expanding public charging infrastructure is critical to the widespread adoption and success of electric vehicles (EVs). Here are the key reasons that highlight its importance:
- Range Confidence:
- Public charging stations provide EV owners with assurance about the availability of charging infrastructure, thereby reducing “range anxiety” – the fear of running out of battery power before reaching the destination. A well-developed network builds confidence among consumers, encouraging more people to consider and adopt electric vehicles.
Urban and Regional Mobility:
- Public charging infrastructure supports urban and regional mobility by enabling longer trips and facilitating inter-city travel. This is important for the acceptance of EVs as practical and versatile vehicles for both daily commutes and occasional longer journeys.
- Access for all:
- Not all EV owners have the ability to charge at home, especially those who live in apartments or without a dedicated parking space. Public charging stations provide an essential charging option for these individuals, promoting inclusivity in the transition to electric transportation.
- Convenience during travel:
- Public charging infrastructure is important for EV drivers when traveling to unfamiliar areas or areas without easy access to home charging. This increases the convenience of electric vehicle use by ensuring that drivers can easily charge their vehicles while on the road.
- Supporting Electric Fleet Adoption:
- Businesses with electric fleets, such as delivery services or ride-sharing companies, rely on a strong public charging infrastructure. Expanding public charging networks encourages more businesses to transition to electric vehicles, thereby reducing overall carbon emissions.
- Promoting Tourism and Economic Development:
- Tourist destinations and business districts benefit from public charging infrastructure as it attracts electric vehicle users. The presence of charging stations encourages tourism, boosts the local economy, and makes areas visionary and sustainable.
- Technological advancements:
- The demand for faster charging solutions and innovative technologies is increasing. The development of public charging infrastructure facilitates the deployment of high-speed chargers, which contributes to reducing overall charging times and improving the convenience of EV ownership.
- Government Incentives and Policies:
- Many governments around the world are encouraging the expansion of public charging infrastructure to meet environmental goals and encourage the adoption of electric vehicles. Public-private partnerships and regulatory support are often key factors in accelerating the development of charging networks.
- Grid Distribution and Load Balancing:
- Strategically placed public charging stations can contribute to better distribution of electricity across the grid. Load balancing and smart charging technologies can be employed to effectively manage power demand, reducing the impact of high demand on the grid.
- In conclusion, expanding public charging infrastructure is critical to mainstream acceptance of electric vehicles, addressing concerns related to range, accessibility, and convenience. It plays an important role in promoting a sustainable and widespread transition from traditional internal combustion vehicles to electric alternatives.
Fast-charging stations and their impact on long-distance travel.
Fast-charging stations play a vital role in facilitating long-distance travel for electric vehicles (EVs), addressing one of the major concerns associated with electric vehicle adoption. Here are the key points highlighting the impact of fast-charging stations on long-distance travel:
Short charging time:
Fast-charging stations are designed to provide higher charging power, which significantly reduces the time required to charge an electric vehicle compared to standard charging stations. This enables EV owners to quickly top up their batteries during long-distance trips, making electric vehicles more practical for travel.
Extended Range Coverage:
With the ability to charge at higher speeds, fast-charging stations extend the effective range of electric vehicles, allowing drivers to cover longer distances in a single day. This is especially important for road trips or commutes that go beyond the normal range of a single charge.
Enhanced Convenience:
Fast-charging stations contribute to the overall convenience of long-distance travel by reducing time spent at charging stations. Drivers can take shorter breaks during their journey, making electric vehicles a more viable and time-efficient option for travel than traditional charging methods.
Strategic Location Planning:
Strategic placement of fast-charging stations on major highways and popular travel routes is essential to support long-distance EV travel. This network plan ensures that drivers have access to fast charging when they need it, thereby promoting the widespread adoption of electric vehicles for inter-city travel.
Interoperability and Standardization:
Efforts to standardize fast-charging connectors and protocols (such as CCS and CHADMO) increase interoperability, allowing a wider range of electric vehicles to use the same charging infrastructure. This standardization simplifies the charging process for users while traveling long distances.
Highway Charging Network:
Fast-charging stations are commonly deployed on highways and express routes, forming networks that connect major cities. This network infrastructure is a key component in promoting electric vehicles as a viable option for long-distance travel, encouraging drivers to choose electric rather than traditional combustion vehicles.
Integration with navigation systems:
Modern electric vehicles and charging infrastructure often feature integrated navigation systems that guide drivers to nearby fast-charging stations. This technology helps drivers plan their routes considering optimal travel time and charging stops for convenience during long journeys.
Economic and Tourism Impact:
The availability of fast-charging stations along highways can have economic benefits for nearby businesses. Additionally, it promotes tourism by making electric vehicles a viable option for travelers, which contributes to the growth of local economies and businesses.
In short, fast-charging stations are a major enabler for long-distance travel in electric vehicles. Their ability to reduce charging time, increase effective range and increase overall convenience plays a key role in encouraging more drivers to adopt electric vehicles for trips beyond their daily commute.
- Safety and Autonomy
4.1 Safety Innovations
- Discuss EV safety features, including advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
- Electric vehicles (EVs) are equipped with a number of safety features, including advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), to enhance driver and passenger safety. Here are some of the key EV safety features, focusing on ADAS:
- Collision Avoidance Systems:
- Forward Collision Warning (FCW): Alerts the driver of an imminent collision with another vehicle or an obstacle in its path.
- Automatic emergency braking (AEB): If a collision is imminent and the driver does not take action, the system may automatically apply the brakes to prevent or mitigate the impact.
- Lane-keeping assistance:
- Lane Departure Warning (LDW): Notifies the driver if the vehicle inadvertently moves out of its lane.
- Lane-keeping assist (LKA): Actively intervenes by steering the vehicle back into its lane if the driver does not respond to warnings.
- Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC):
- Maintains a set speed but can also automatically adjust vehicle speed to maintain a safe distance from the car in front.
- Blind spot detection:
- Alerts the driver when there is a vehicle in the blind spot, usually through visual or audible warnings.
- Cross-Traffic Alert:
- Warns the driver about oncoming traffic from the side, especially when backing out of parking spaces.
- Parking Assistance:
- 360-degree camera system: Provide a bird’s-eye view of the vehicle to aid in parking in tight spaces.
- Automated parking systems: Some EVs are equipped with systems that can automatically steer the vehicle into a parking space.
- Driver attention monitoring:
- Monitors driver behaviour and issues alerts if signs of fatigue or inattention are detected.
- Pedestrian detection:
- Uses sensors and cameras to detect pedestrians in or near the vehicle’s path and can trigger warnings or automatic braking to prevent a collision.
- Traction Control and Stability Control:
- Increase vehicle stability and prevent slipping in various driving conditions.
- Battery Protection Systems:
- EVs include safety features to protect the battery, including thermal management systems to control temperatures and prevent overheating.
- Structural Safety:
- EVs are designed with strong and rigid structures to protect passengers in the event of a collision. Battery packs are often located in protected areas of the vehicle.
- Cyber Security Measures:
- As EVs become more connected, manufacturers implement cybersecurity measures to protect against potential cyber threats, ensuring the security of the vehicle’s systems.
- These safety features collectively contribute to making electric vehicles not only eco-friendly but also safe on the road. As technology advances, the integration of more sophisticated ADAS will further enhance the safety of EVs, paving the way for increased autonomous driving capabilities.
Common misconceptions about EV safety.
- Despite the many safety features and advancements in electric vehicles (EVs), there are still some common misconceptions. Let’s look at some of these misconceptions:
- Danger of electric shock:
- Myth: There is a perception that EVs have a higher risk of electric shock, especially in the event of a collision or while charging.
- Reality: EVs follow stringent safety standards. In the event of a crash, EVs are designed to automatically disconnect the battery, reducing the risk of electric shock. Additionally, the charging system is designed with safety features to prevent electrical shock hazards.
- Battery fire and explosion:
- Myth: Some people fear that EV batteries pose a risk of fire or explosion.
- Reality: While any vehicle with a fuel source, including gasoline cars, is at risk of fire, EVs are required to undergo extensive safety testing. The design of EV battery packs includes features to reduce the risk of thermal events, and incidents are extremely rare. Emergency responders are trained to safely handle EV-related incidents.
- Battery degradation and long-term protection:
- Misconception: Concerns exist about the long-term safety of EV batteries, particularly regarding degradation and potential hazards as batteries age.
- Reality: Manufacturers implement rigorous testing and quality control measures to ensure the longevity and safety of EV batteries. Battery management systems actively monitor and manage cell health, and safety margins are built into the design to account for degradation over time.
- Weight and crash protection:
- Myth: Some people believe that the weight of EV batteries makes these vehicles less safe in a collision.
- Reality: EVs are designed with safety in mind, and weight distribution often increases stability and crash safety due to less battery space. To meet safety standards, EVs have to undergo the same rigorous crash tests as conventional vehicles.
- Limited emergency response knowledge:
- Misconception: Concerns are raised about the ability of emergency responders to handle accidents involving EVs due to unfamiliarity with electrical systems.
- Reality: Emergency responders receive training in handling electric vehicles. Manufacturers provide resources and guidelines to ensure responders can safely manage incidents involving EVs, including protocols for battery disconnection and handling.
- Environmental impact of battery production:
- Misconception: Some argue that the environmental impact of manufacturing EV batteries outweighs their overall environmental benefits.
- Reality: Although battery production has an environmental impact, continued progress is being made to improve the sustainability of battery manufacturing. Over the lifetime of an EV, reduced emissions from driving may outweigh the initial environmental impact of battery production.
- Addressing these misconceptions helps provide a more accurate understanding of the safety aspects of electric vehicles, promoting informed decision making and allaying unjustified concerns about their safety.
4.2 Autonomous Driving
- Explore how EVs are at the forefront of autonomous technology.
- Electric vehicles (EVs) are at the forefront of autonomous technology, playing a key role in the development and integration of self-driving features. Here are the key aspects that explain how EVs are advancing autonomous technology:
- Sensor Integration:
- EVs are often equipped with advanced sensor suites, including cameras, radar, lidar, and ultrasonic sensors. These sensors are essential to provide the vehicle with real-time data about its surroundings, a critical component for autonomous driving.
- High performance Computing:
- Electric vehicles are equipped with powerful onboard computers capable of processing large amounts of data in real time. These computing systems are necessary to run the complex algorithms and decision-making processes required for autonomous driving.
- Over-the-air updates:
- Many electric vehicle manufacturers use over-the-air (OTA) update capabilities. This feature allows remote installation of software updates, making continuous improvements to autonomous driving systems possible as new algorithms and functionality are developed.
- Energy efficiency and range optimization:
- Electric vehicles are inherently designed to be energy-efficient, and this efficiency extends to autonomous driving systems. Optimizing energy consumption is important to extend the range of EVs, making them suitable for autonomous technologies that require continuous power.
- Integration with Sustainable Transportation Solutions:
- The combination of electric propulsion and autonomous technology aligns with the overarching goal of creating sustainable and efficient transportation systems. EVs with autonomous capabilities can contribute to reducing traffic congestion, improving energy efficiency, and reducing emissions.
- Innovation in self-parking:
- Many electric vehicles have advanced self-parking capabilities. These innovations allow the vehicle to navigate autonomously and park in designated locations, demonstrating the potential for further autonomous advancements in real-world scenarios.
- Development Partnership:
- Electric vehicle manufacturers often collaborate with technology companies and startups specializing in autonomous driving. These partnerships leverage the expertise of both industries, accelerating the development and integration of autonomous features into electric vehicles.
- Autonomous Electric Fleet:
- Companies envisioning autonomous ride-sharing services or delivery fleets often select electric vehicles for their autonomous platforms. The combination of autonomy and electric propulsion aligns with the future vision of sustainable, driverless transportation services.
- safety considerations:
- The safety-conscious nature of electric vehicle design meshes well with the safety requirements of autonomous driving. Both technologies give priority to reducing accidents and increasing overall road safety.
- Regulatory and Legislative Support:
- Governments and regulatory bodies recognize the potential benefits of autonomous technology. In many cases, they are supportive of initiatives that promote the integration of electric vehicles with autonomous capabilities, creating a favorable environment for development and deployment.
- As technology advances, the integration of electric vehicles and autonomous features is evolving, making EVs important in shaping the future of transportation. The combination of clean energy and autonomous driving has the potential to revolutionize the way people move, providing safer, more efficient and environmentally friendly transportation solutions.
- Touch on Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (FSD) and other developments.
- Recent Update (as of February 26, 2024):
- Tesla FSD Beta v12: Recently, Tesla expanded its FSD beta program to a wider range of users in North America. This version offers features like automatic U-turn but temporarily removes traffic-aware cruise control for testing and safety measures.
- Regulatory landscape: Discussions and regulations related to autonomous vehicles are constantly evolving. While some regions consider limited deployment, widespread adoption still faces obstacles due to security concerns and infrastructure requirements.
- Competition: Many companies, including traditional carmakers and tech giants, are actively developing and testing autonomous driving technologies, contributing to a more competitive landscape.
- Tesla’s evolving scenario of full self-driving (FSD) and autonomous driving
- Tesla’s FSD, a suite of driver-assist features that eventually aim for full autonomy, continues to generate significant interest. Although the core information of the article remains relevant, the inclusion of recent updates increases its accuracy and comprehensiveness.
- key points:
- Tesla FSD: Offers features like Autopilot, Navigate on Autopilot, and Traffic Light/Stop Sign Control, aiming toward full autonomy.
- Autopilot updates: Tesla continues to improve Autopilot through regular over-the-air updates, enhancing vehicle recognition, navigation, and overall performance.
- Beta Testing: Tesla’s FSD beta program has expanded, collecting real-world data and user feedback to refine the system.
- Hardware advancements: Tesla vehicles use advanced hardware to support autonomous driving, with continuous improvements being made.
- Regulatory landscape: Autonomous vehicle regulations remain dynamic, with deployment being approached cautiously for safety reasons in different regions.
- Competition and Industry Developments: Many competitors are actively developing and testing autonomous driving technologies, fostering a competitive and rapidly evolving landscape.
- Challenges and Security Concerns: Ensuring the safety and reliability of autonomous systems is paramount, requiring continuous testing and development efforts.
- Public perception and education: Public awareness and education about the capabilities and limitations of autonomous driving technology is critical for responsible and safe use.
- Stay up to date:
- The field of autonomous driving is constantly evolving. It is essential to regularly follow industry news and updates on companies like Tesla and its competitors to stay informed about the latest developments and ongoing challenges.
- By incorporating these updates and maintaining a future-oriented perspective, this article provides a more accurate and insightful overview of Tesla’s FSD and the broader landscape of autonomous driving.
The Future Landscape: What Lies Ahead
5.1 Beyond Cars: Electrification in Other Sectors
- Talking about electric buses, trucks, and two-wheelers.
The expansion of electric vehicles (EVs) has expanded beyond passenger cars, with electric buses, trucks and two-wheelers becoming increasingly prevalent. Here’s an overview of developments in each category:
Electric Buses:
Public transport solutions: Many cities around the world are adopting electric buses as part of their public transport fleets. Electric buses provide environmental benefits by reducing emissions, improving air quality and contributing to sustainable mobility solutions in urban areas.
Longer range options: Electric bus manufacturers are developing models with extended range, allowing all-day operation on a single charge. Fast-charging infrastructure is also being deployed at bus terminals to reduce downtime.
Electric Truck:
Commercial freight and delivery: Electric trucks are gaining popularity in the freight and delivery sector, providing a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to traditional diesel-powered vehicles. Companies are investing in electric trucks for last-mile delivery and short-distance transportation.
Lower operating costs: While electric trucks may have higher upfront costs, they often offer lower operating costs over their lifetime. Electric trucks benefit from lower fuel costs, simplified maintenance and potential government incentives.
Electric two-wheeler:
Scooters and motorcycles: Electric scooters and motorcycles are becoming increasingly popular for commuting in urban areas. They provide a cost-effective and environment-friendly alternative to two-wheelers with conventional internal combustion engines.
Light Electric Vehicles (LEV): Light electric vehicles, including electric bicycles and e-scooters, have been widely adopted in many cities. They are often used for short distance travel, providing a convenient and sustainable mode of transportation.
Charging Infrastructure:
Expansion to commercial vehicles: The growth of electric buses and trucks requires the development of dedicated charging infrastructure. Charging stations designed for larger commercial vehicles are being deployed to support the electrification of public transport and freight fleets.
Urban Charging Network: Charging infrastructure for electric two-wheelers is generally found in urban areas, with charging stations strategically placed to cater to the short range nature of these vehicles.
Battery Technology: Advances in range and efficiency: Ongoing advancements in battery technology contribute to increased range and efficiency for electric buses, trucks and two-wheelers. Improved energy density and fast-charging capabilities increase the practicality and feasibility of electric options
Government Initiatives and Incentives:
Promoting adoption: Many governments are launching incentives and initiatives to promote the adoption of electric buses, trucks and two-wheelers. These may include subsidies, tax incentives, and regulatory measures to encourage the transition to cleaner and more sustainable transportation.
Integration of Smart Technologies:
Connectivity and telematics: Electric commercial vehicles often integrate smart technologies for efficient fleet management. Telematics systems provide real-time data on vehicle performance, energy consumption and maintenance needs, contributing to improved operational efficiency.
Electrification of buses, trucks and two-wheelers is an important aspect of the broader shift towards sustainable and eco-friendly transportation. As technology advances and charging infrastructure expands, electric options in these categories could play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of urban mobility and logistics.
- Mention the electrification of shipping and aviation.
The electrification of shipping and aviation represents a significant shift towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation solutions.
Electrification of Shipping:
Electric Ships: Several initiatives are underway to develop and deploy electric ships. Battery-electric and hybrid-electric propulsion systems are being explored to reduce reliance on traditional fossil fuels. These technologies aim to reduce emissions, reduce fuel consumption and contribute to cleaner oceans.
Coastal power: Ports are increasingly adopting coastal power, also known as cold ironing or alternative marine power (AMP). This allows ships to turn off their engines when docked and connect to the local electrical grid, reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
Electrification of Aviation:
Electric Aircraft: Research and development is going on in the field of electric aviation. Electric aircraft and urban air mobility (UAM) vehicles are being designed and tested to take advantage of electric propulsion systems. These technologies have the potential to reduce carbon emissions and noise pollution.
Hybrid-electric solutions: Hybrid-electric aircraft combining conventional combustion engines with electric propulsion are also being explored. This approach aims to increase fuel efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of air travel.
Infrastructure development: The electrification of aviation requires the development of supporting infrastructure, including electric charging stations for aircraft. Airports are beginning to invest in these facilities to accommodate the growing interest in electric aviation.
Both industries face challenges in terms of energy storage, infrastructure development and the need for advancements in battery technology to make large-scale electrification possible. Despite these challenges, electrification of shipping and aviation is an important step towards achieving more sustainable and eco-friendly transportation solutions in global efforts to combat climate change.
5.2 Challenges and Opportunities
- Address range anxiety, battery recycling, and grid capacity.
Range Concern:
Improvements in battery technology: Continued advancements in battery technology are essential to increase the range of electric vehicles (EVs) and reduce range anxiety. Research and development efforts are focused on increasing energy density, increasing charging speed, and optimizing overall battery performance.
Expansion of charging infrastructure: Widespread deployment of fast-charging stations can reduce range anxiety by providing convenient access to charging points. Governments, businesses and communities are investing in expanding charging networks to support the growing adoption of electric vehicles.
Battery Recycling:
Establishing recycling infrastructure: Developing strong battery recycling infrastructure is important for managing the end life cycle of batteries. Governments and industries should cooperate to establish efficient recycling systems, ensuring the collection, transportation and processing of used batteries in an environmentally responsible manner.
Promoting the circular economy: Encouraging a circular economy approach includes designing batteries for recyclability from the beginning. Manufacturers can prioritize the use of recyclable materials, simplify battery disassembly, and implement processes that facilitate the recovery of valuable components.
Grid Capacity:
Smart Grid Solutions: Implementing smart grid technologies can optimize grid capacity by intelligently managing energy distribution and consumption. Smart grids enable real-time communication between utilities and consumers, allowing better load balancing and more efficient use of available capacity.
Grid upgrades and expansion: Investments in upgrading and expanding the electrical grid are necessary to accommodate increased demand as a result of widespread electrification. Modernizing infrastructure, integrating renewable energy sources, and incorporating energy storage solutions contribute to a more flexible and efficient grid.
Tackling these challenges requires a multi-pronged approach that includes technological innovation, policy support and collaborative efforts between industry stakeholders, governments and communities. As progress continues and collective efforts are intensified, these challenges associated with electric vehicles and renewable energy adoption can be effectively mitigated.
Job opportunities in the EV industry.
The electric vehicle (EV) industry is experiencing rapid growth, creating vast employment opportunities across various sectors. Here are some of the key sectors where job opportunities are emerging:
Engineering and Research:
Battery Technology: Engineers with expertise in battery technology are in high demand. This includes research and development of advanced battery chemistries, materials and energy storage solutions.
Vehicle Design and Manufacturing: Developing and manufacturing electric vehicles requires engineers and designers. This includes designing efficient electric drivetrains, lightweight materials and aerodynamic structures.
Software and Electronics:
Embedded Systems: Since EVs are heavily dependent on electronic control systems, there is a demand for professionals skilled in embedded systems development for vehicle control units, battery management systems, and software integration.
Autonomous Driving: With the integration of autonomous features into EVs, the demand for experts in artificial intelligence, machine learning and sensor technologies is increasing.
Charging Infrastructure:
Installation and maintenance: As charging infrastructure expands, technicians and maintenance personnel are needed to install, monitor, and maintain charging stations.
Infrastructure planning: Urban planners and project managers need to strategically plan and implement charging infrastructure networks.
sales and marketing:
EV Sales Reps: With the growing popularity of electric vehicles, automotive companies need sales professionals with knowledge of EV technology to educate customers and boost sales.
Marketing experts: Companies are hiring marketing experts to create awareness about electric vehicles and highlight their environmental and economic benefits.
Policy and Advocacy:
Policy Analysts: Governments and non-profit organizations hire professionals to analyze and develop policies that support the growth of the EV industry, including incentives, regulations, and infrastructure development.
Advocacy and communications: Organizations focused on sustainable transportation often need individuals to advocate for EV adoption and explain the benefits to various stakeholders.
Supply Chain and Logistics:
Supply Chain Management: Professionals are needed to manage the supply chain of EV components to ensure smooth flow of materials for manufacturing.
Logistics and Distribution: With the global nature of the industry, there are opportunities in logistics and distribution to efficiently transport EV components and vehicles.
Energy and Stability:
Renewable energy experts: Since EVs aim to reduce carbon emissions, experts in renewable energy sources are needed to ensure sustainable and clean energy production for the charging
infrastructure.
The EV industry offers a wide variety of employment opportunities, attracting individuals from different educational backgrounds and skill sets. As the industry evolves, new roles and specializations are likely to emerge, providing a dynamic and exciting job market for professionals interested in sustainable transportation.
In conclusion, the advent of the electric car era marks more than just a change in transportation; It marks a paradigm shift with far-reaching impacts on our environment, economy and daily life. As we see the rise of electric vehicles, we are not only upgrading our ways of traveling but also actively contributing to a cleaner, smarter future.
This transformative journey is characterized by innovations in battery technology, advances in sustainable energy and the proliferation of electric vehicle infrastructure. In addition to reducing our dependence on fossil fuels, electric cars play an important role in mitigating climate change and promoting environmental sustainability.
Economically, the electric vehicle industry has become a driving force for job creation, increasing opportunities in a variety of sectors ranging from engineering and manufacturing to software development and sales. As governments and businesses invest in the electrification of transportation, the impact is felt across supply chains, urban planning, and renewable energy development.
On a day-to-day basis, the electric car era reshapes our daily routines, affecting the way we refuel, travel and interact with our surroundings. The rise of electric vehicles encourages the shift toward clean energy sources and reinforces the importance of sustainability in our collective consciousness.
As we move forward on this electrification journey, it is important to remain committed to the principles of environmental stewardship and technological innovation. Gear up for a future where electric cars are not just vehicles but symbols of progress, a commitment to a cleaner, smarter and more sustainable world.

Pingback: Jeep Electric Vehicles: Driving into the Future with Zero Emissions Freedom - allnichespectrum
Pingback: Advantage and Disadvantage of Hybrid Car - allnichespectrum
Несомненно стильные события индустрии.
Исчерпывающие эвенты самых влиятельных подуимов.
Модные дома, бренды, haute couture.
Свежее место для стильныех людей.
https://fashionablelook.ru
Абсолютно свежие новости модного мира.
Важные события мировых подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, гедонизм.
Свежее место для трендовых людей.
https://modavgorode.ru
Полностью стильные новости подиума.
Все мероприятия всемирных подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, гедонизм.
Приятное место для стильныех людей.
https://modaizkomoda.ru
Очень стильные новости индустрии.
Абсолютно все эвенты всемирных подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, высокая мода.
Самое лучшее место для модных хайпбистов.
https://myfashionacademy.ru/
Абсолютно трендовые события модного мира.
Абсолютно все новости известнейших подуимов.
Модные дома, бренды, гедонизм.
Самое лучшее место для стильных хайпбистов.
https://metamoda.ru/moda/599-doja-cat-vyzvala-bezumie-v-tope-i-yubke-iz-pishchevoy-plenki-s-rezhisserom-vetements-guram-gvasalia/
Очень свежие новости индустрии.
Исчерпывающие мероприятия лучших подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, высокая мода.
Свежее место для трендовых хайпбистов.
https://hypebeasts.ru/
Полностью свежие события модного мира.
Абсолютно все мероприятия мировых подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, haute couture.
Новое место для модных людей.
https://luxe-moda.ru/chic/162-loro-piana-lyubimyy-brend-politikov-i-biznesmenov/
Точно стильные события моды.
Абсолютно все мероприятия лучших подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, высокая мода.
Лучшее место для модных хайпбистов.
https://rftimes.ru/news/2024-07-05-teplye-istorii-brend-herno
Несомненно актуальные новинки мира fashion.
Исчерпывающие новости лучших подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, высокая мода.
Новое место для модных хайпбистов.
https://balmain1.ru/balmain/381-kak-otlichit-originalnyy-balmain-ot-poddelki/
Pingback: Are Electric Cars Better For The Environment -
Самые актуальные новинки модного мира.
Абсолютно все мероприятия всемирных подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, высокая мода.
Интересное место для трендовых хайпбистов.
https://qrmoda.ru/fashion/361-manzoni-24-italyanskiy-mehovoy-shik/
Наиболее трендовые новости мира fashion.
Все новости всемирных подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, haute couture.
Свежее место для трендовых людей.
https://stylecross.ru/read/2024-06-19-lacoste-kachestvennyy-premium-po-tsene-mass-marketa/
Наиболее стильные новинки индустрии.
Актуальные мероприятия всемирных подуимов.
Модные дома, бренды, высокая мода.
Самое лучшее место для стильныех хайпбистов.
https://world.lepodium.net/
Абсолютно свежие события мира fashion.
Важные эвенты мировых подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, haute couture.
Самое лучшее место для трендовых людей.
https://rftimes.ru/news/2024-08-14-7-samyh-kultovyh-veshchey-ot-balenciaga
Несомненно важные новинки моды.
Абсолютно все новости мировых подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, гедонизм.
Лучшее место для модных людей.
https://hypebeasts.ru/stuff/2024-08-18-demna-gvasaliya-ikona-sovremennoy-mody/
Самые стильные новости мировых подиумов.
Исчерпывающие новости лучших подуимов.
Модные дома, бренды, гедонизм.
Самое приятное место для стильныех людей.
https://chelyabinsk.rftimes.ru/news/2024-07-07-huligany-povredili-trolleybus-v-chelyabinske-postradala-passazhirka
Абсолютно стильные новости моды.
Исчерпывающие мероприятия лучших подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, высокая мода.
Новое место для трендовых хайпбистов.
https://kostroma.rftimes.ru/news/2024-07-01-rebenok-v-kostrome-poluchil-sereznuyu-travmu-povisnuv-na-zabore-so-shtyrem
https://novosibirsk.rftimes.ru/news/2024-04-19-v-novosibirske-v-ramkah-programmy-remonta-shkol-rekonstruiruetsya-shkola-77
https://murmansk.rftimes.ru/news/2024-04-11-itogi-chempionata-norvegii-trassy-murmanska-korolevskie
https://sochidaily.ru/read/2024-03-01-samolet-iz-peterburga-v-sochi-vernuli-v-pulkovo.html
https://sevastopol.rftimes.ru/news/2024-06-13-v-sevastopole-otrazili-raketnuyu-ataku-vsu-vse-tseli-unichtozhili-v-vozduhe-postradavshih-i-razrusheniy-net
Полностью трендовые новости индустрии.
Все события мировых подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, высокая мода.
Новое место для трендовых хайпбистов.
https://kazantoday.ru/kznpub/2024-03-01-chempionat-rossii-po-hokkeyu-s-myachom.html
0901 https://vladnews.ru/2023-11-16/227949/demna_gvasaliya https://msk.rftimes.ru/news/2024-05-29-tragediya-v-rezultate-operatsii-22-letnyaya-studentka-iz-ufy-umerla-ot-sepsisa
https://vladtoday.ru/news/2024-01-22-padenie-temperatury-na-16-gradusov-vo-vladivostoke/
https://rftimes.ru/news/2024-04-14-prirost-zabolevaemosti-koronavirusom-protivoyadie-kotorogo-ne-zhdali-mediki-obespokoeny-vspyshkoy-virusa
https://sochidaily.ru/read/2023-12-08-stroyashchiysya-v-sochi-tsentr-vosstanovleniya-sportsmenov.html
Самые трендовые новости моды.
Актуальные события мировых подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, гедонизм.
Свежее место для стильныех людей.
https://murmansk.rftimes.ru/news/2024-06-24-novoispechennyy-glavnyy-sudebnyy-pristav-prikamya
https://cheboksary.rftimes.ru/news/2024-07-09-kristina-makarenko-oderzhala-pobedu-na-kubke-rossii-v-legkoy-atletike
https://ekbtoday.ru/news/2024-03-01-vrach-iz-ekaterinburga-perevela-moshennikam-pochti-3-mln-rubley/
https://mskfirst.ru/msk/2024-01-13-ustanovlena-lichnost-zhenshchiny-naydennoy-ubitoy-na-vostoke-moskvy
https://mskfirst.ru/msk/2023-11-27-moskvarium-prinyat-obitateley-sevastopol
Точно свежие новости модного мира.
Актуальные эвенты известнейших подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, гедонизм.
Приятное место для трендовых людей.
https://spb.rftimes.ru/news/2024-04-13-provedeno-sravnitelnoe-issledovanie-populyarnogo-seriala-igra-prestolov
https://emurmansk.ru/pub/2023-12-13-gorsovet-murmanska-prinyal-uchastie-v-aktsii-podari-detyam-schaste/
4439 https://vladnews.ru/2023-11-16/227949/demna_gvasaliya https://ekbtoday.ru/news/2024-08-05-razvitie-transportnoy-infrastruktury-ekaterinburga/
https://novosibirsk.rftimes.ru/news/2024-05-17-razvitie-promyshlennogo-turizma-gotovy-prisoedinitsya-desyatki-novosibirskih-predpriyatiy
https://ekaterinburg.rftimes.ru/news/2024-04-21-novosti-o-gryadushchem-kosmicheskom-proekte-missiya-na-lunu-vozvrashchenie-domoy
Точно важные новости модного мира.
Все новости лучших подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, высокая мода.
Приятное место для модных людей.
https://sochidaily.ru/read/2024-02-04-pervyy-reys-tu-214-posle-vozobnovleniya-poletov.html
https://ivanono.rftimes.ru/news/2024-04-09-spetsoperatsiya-z-hronika-glavnyh-voennyh-sobytiy-8-aprelya
https://ryazansport.ru/sport/metareytingi-budut-vpervye-ispolzovany-na-olimpiyskih-igrah-2024-goda.html
https://mskfirst.ru/msk/2024-01-05-vozobnovleno-teplosnabzhenie-domov-na-severo-vostoke-moskvy
https://sport.mskfirst.ru/msk/2024-07-07-chempionat-finlyandii-match-oulu-sik
Полностью важные новости индустрии.
Абсолютно все новости мировых подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, высокая мода.
Новое место для модных хайпбистов.
https://mskfirst.ru/msk/2023-12-26-kolichestvo-zaderzhannyh-po-predprinimatelskim-statyam-v-moskve
https://enovosibirsk.ru/read/2024-02-06-dorozhnye-izmeneniya-v-novosibirske-nadeyutsya-li-na-uluchshenie-situatsii/
https://omskdaily.ru/news/2024-07-22-vosmiletney-devochke-iz-omska-vnov-nachislili-chuzhie-dolgi/
https://omskdaily.ru/news/2024-02-08-sychev-o-prodvizhenii-futbola-v-omske/
https://khabarovsk.rftimes.ru/news/2024-04-09-avariynaya-posadka-vertoleta-mi-8-v-habarovskom-krae
Самые актуальные новости мира fashion.
Исчерпывающие эвенты мировых подуимов.
Модные дома, бренды, haute couture.
Приятное место для трендовых людей.
0901 https://vladnews.ru/2023-11-16/227949/demna_gvasaliya https://msk.rftimes.ru/news/2024-05-29-tragediya-v-rezultate-operatsii-22-letnyaya-studentka-iz-ufy-umerla-ot-sepsisa
https://kursktoday.ru/news/2023-11-26-podrostok-razbil-steklo-i-pohitil-iz-zakusochnoy-platezhnyy-terminal-i-dengi
https://sevastopol.rftimes.ru/news/2024-06-13-v-sevastopole-otrazili-raketnuyu-ataku-vsu-vse-tseli-unichtozhili-v-vozduhe-postradavshih-i-razrusheniy-net
https://sochidaily.ru/read/2024-03-01-samolet-iz-peterburga-v-sochi-vernuli-v-pulkovo.html
https://sochidaily.ru/read/2024-03-04-massovoe-dtp-v-sochi-tri-postradavshih.html
I’m still learning from you, as I’m improving myself. I definitely enjoy reading all that is posted on your site.Keep the tips coming. I loved it!
Самые важные новинки мировых подиумов.
Актуальные новости лучших подуимов.
Модные дома, лейблы, гедонизм.
Приятное место для модных хайпбистов.
https://rftimes.ru/news/2023-11-24-meteozavisimost-kakie-produkty-nuzhno-isklyuchit-iz-ratsiona
https://simferopol.rftimes.ru/news/2024-05-31-zheleznodorozhnyy-marshrut-moskva-simferopol-voshel-v-top-napravleniy-puteshestviy-v-pervyy-den-leta
https://krasnodar.rftimes.ru/news/2024-03-03-zastrelivshego-opponenta-v-krasnodare-muzhchinu-otpravili-pod-strazhu
https://mskfirst.ru/msk/2024-03-22-servis-vmeste-s-kulturoy-pomog-organizovat-v-moskve-25-tysyach-meropriyatiy
https://kazantoday.ru/kznpub/2023-12-02-bolee-tysyachi-dtp-zafiksirovano-v-kazani-v-tekushchem-godu.html
Точно трендовые события индустрии.
Актуальные новости самых влиятельных подуимов.
Модные дома, бренды, высокая мода.
Интересное место для модных хайпбистов.
https://emurmansk.ru/pub/2024-05-31-avariynaya-posadka-samoleta-iz-peterburga-v-murmanske/
Абсолютно стильные события мировых подиумов.
Абсолютно все новости самых влиятельных подуимов.
Модные дома, торговые марки, haute couture.
Приятное место для модных людей.
https://vladtoday.ru/news/2023-12-27-mezhdunarodnyy-aeroport-vladivostok-otmetil-2-5-mln-passazhirov-v-2023-godu/
Модные заметки по выбору крутых видов на любой день.
Статьи профессионалов, события, все новые коллекции и мероприятия.
https://rftimes.ru/news/2024-08-14-7-samyh-kultovyh-veshchey-ot-balenciaga
Модные заметки по подбору модных видов на каждый день.
Мнения стилистов, новости, все новинки и мероприятия.
https://julistyle.ru/moda/2024-05-01-jaeger-lecoultre-predstavila-novyy-hronograf-s-fazoy-luny-i-dnevnoy-nochyu/
Стильные заметки по выбору отличных видов на каждый день.
Заметки экспертов, события, все новые коллекции и мероприятия.
https://urban-moda.ru/all/749-za-chto-my-lyubim-brend-coach-ikona-amerikanskogo-stilya-i-masterstva/